100. Same Tree
Description
Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
Example 1:
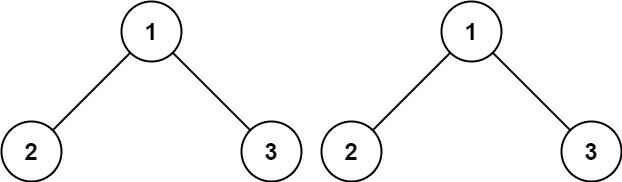
- Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
- Output: true
Example 2:
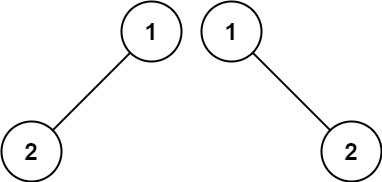
- Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
- Output: false
Example 3:
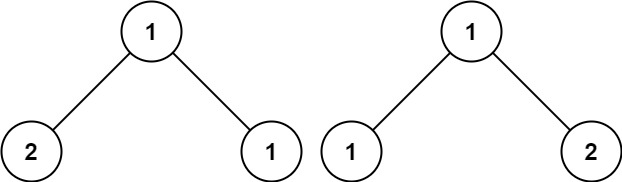
- Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
- Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in both trees is in the range [0, 100].
- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def isSameTree(self, p, q):
"""
:type p: Optional[TreeNode]
:type q: Optional[TreeNode]
:rtype: bool
"""
stack_rights = []
while p or q or stack_rights:
if (p is None or q is None) or (p.val != q.val): # 둘 중 하나가 None이거나 값이 다르면 false
return False
if p.right is not None and q.right is not None: # 둘 다 오른쪽 자식이 있으면 스택에 추가
stack_rights.append((p.right, q.right))
elif p.right is not None or q.right is not None: # 한 쪽만 오른쪽 자식 존재하면 false
return False
if p.left is not None and q.left is not None: # 둘 다 왼쪽 자식이 있으면 이동
p = p.left
q = q.left
elif p.left is None and q.left is None: # 둘 다 왼쪽 자식이 없고
if stack_rights: # 스택에 값이 있다면 pop
p, q = stack_rights.pop()
else: # 스택에 값이 없다면 None으로 반환
p = None
q = None
else: # 한 쪽만 왼쪽 자식이 존재하면 false
return False
return True
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 12.51 MB | Beats 40.19%
DFS (깊이 우선 탐색) 방식을 사용했다. 시간 복잡도를 최대한 줄이고 싶어서 재귀 호출 대신 스택으로 구현해봤다. 효율은 좋았지만 코드가 너무 길어졌다.
트리 노드의 구조를 출력해보면 다음과 같다.
print(p) 예시
e.g.1 → TreeNode{
val: 1,
left: TreeNode{val: 2, left: None, right: None},
right: TreeNode{val: 3, left: None, right: None}
}
e.g.2 → TreeNode{val: 2, left: None, right: None}
e.g.3 → None
p.val로 val 값만 추출 가능- 두 노드의 값을 비교하려면 val 값만 추출해야 한다(노드 자체끼리 비교하면 에러 발생)
None인 노드의 val 값을 출력하려 할 경우 에러 발생
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def isSameTree(self, p: Optional[TreeNode], q: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not p and not q: # both trees are empty
return True
if p and q and p.val == q.val: # both trees are non-empty and have the same root value
return self.isSameTree(p.left, q.left) and self.isSameTree(p.right, q.right)
return False # none of the above conditions are met
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
재귀 호출을 이용했으며, 두 트리가 동일한 케이스 두 가지일 경우만 True를 반환하고 나머지는 false가 되는 원리다.
- 두 트리가 모두 빈 트리일 경우
- 두 트리가 비어 있지 않고, 값이 같은 경우
- 재귀적으로 두 트리의 왼쪽 서브트리와 오른쪽 서브트리를 비교
- 왼쪽 자식들(서브트리)과 오른쪽 자식들이 모두 True가 나와야 and 비교연산자의 결과도 True
2nd
class Solution:
def isSameTree(self, p: Optional[TreeNode], q: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
stack = [(p, q)] # 스택에 두 트리의 루트 노드를 추가
while stack: # 스택이 빌 때까지 반복
p, q = stack.pop()
if p or q:
if not p or not q or p.val != q.val:
return False
stack.append((p.left, q.left)) # 왼쪽 자식 비교
stack.append((p.right, q.right)) # 오른쪽 자식 비교
return True
내가 제출했던 것처럼 스택을 이용했으나, 좀 더 간단한 방법이어서 참고했다. 다만 같은 깊이에서 왼쪽 자식부터 비교하는게 더 편해서 스택에 넣는 순서를 변경하면 더 좋을 것 같다.
3rd
class Solution:
def isSameTree(self, p: Optional[TreeNode], q: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
return str(p)==str(q)
TreeNode 타입을 str로 형변환이 가능하다는 것을 알게 된 답안이어서 참고했다.
4rd
class Solution(object):
def isSameTree(self, p, q):
queue = [(p, q)]
while queue:
node1, node2 = queue.pop(0)
if not node1 and not node2:
continue
elif None in [node1, node2]:
return False
else:
if node1.val != node2.val:
return False
queue.append((node1.left, node2.left))
queue.append((node1.right, node2.right))
return True
큐(queue)를 이용한 너비 우선 탐색 방식으로도 풀 수 있다. 파이썬의 collections 모듈에서 제공하는 deque로 큐를 구현할 수 있다.
💡 deque(덱, Double-Ended Queue)
from collections import deque
- 양방향에서 삽입/삭제 가능 →
append(),appendleft(),pop(),popleft() - 리스트의
pop()보다 빠른 연산 가능 - 스택과 큐 모두 구현 가능



Leave a comment