1022. Sum of Root To Leaf Binary Numbers
Description
You are given the root of a binary tree where each node has a value 0 or 1. Each root-to-leaf path represents a binary number starting with the most significant bit.
- For example, if the path is
0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1, then this could represent01101in binary, which is13.
For all leaves in the tree, consider the numbers represented by the path from the root to that leaf. Return the sum of these numbers.
The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bits integer.
Example 1:
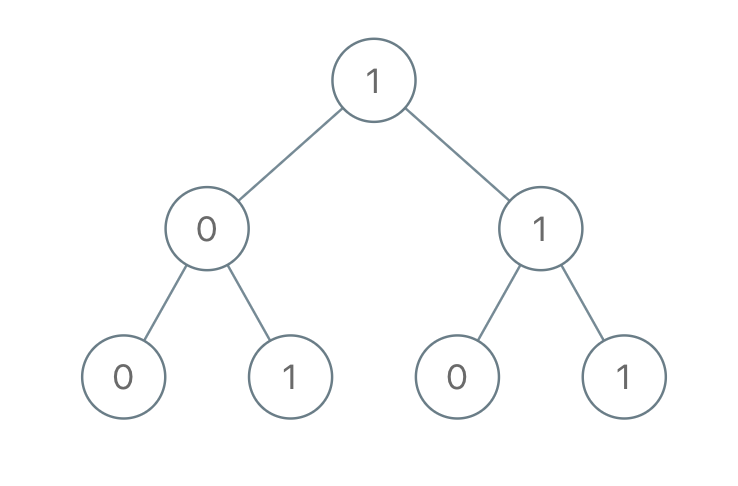
- Input: root = [1,0,1,0,1,0,1]
- Output: 22
- Explanation: (100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22
Example 2:
- Input: root = [0]
- Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. Node.valis0or1.
💡 Hint 1:
Find each path, then transform that path to an integer in base 10.
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumRootToLeaf(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
result = 0
stack = [(0, root)] # (누적 합계, 현재 노드)
while stack:
prev, node = stack.pop()
curr = (prev * 2) + node.val
if not node.left and not node.right: # 잎노드
result += curr
if node.right:
stack.append([curr, node.right])
if node.left:
stack.append([curr, node.left])
return result
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 17.99 MB | Beats 90.01%
스택을 이용하여 각 root-to-leaf path를 순회하고 누적 합계를 저장할 수 있다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def sumRootToLeaf(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def sumRootToLeaf(root, res): # here; "res" is "sum"
if root == None: return 0
res = (2 * res) + root.val
if root.left == None and root.right == None: return res
return sumRootToLeaf(root.left, res) + sumRootToLeaf(root.right, res)
return sumRootToLeaf(root, 0)
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(ℎ)
재귀 호출로 푸는 방법도 참고했다.



Leave a comment