110. Balanced Binary Tree
Description
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
Example 1:
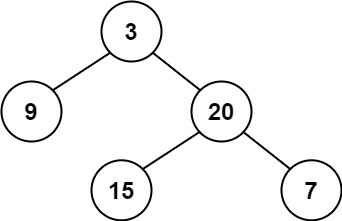
- Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
- Output: true
Example 2:
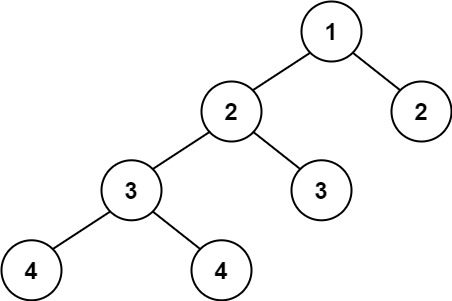
- Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
- Output: false
Example 3:
- Input: root = []
- Output: true
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def isBalanced(self, root):
"""
:type root: Optional[TreeNode]
:rtype: bool
"""
def compare_depth(root):
if root is None:
return 0 # 빈 노드일 경우 깊이에 +0
left_depth = compare_depth(root.left) # 왼쪽 서브트리 깊이 계산
right_depth = compare_depth(root.right) # 오른쪽 서브트리 깊이 계산
# 왼쪽 서브트리나 오른쪽 서브트리가 이미 불균형이거나 두 서브트리 깊이의 차이가 2 이상(불균형)
if left_depth == -1 or right_depth == -1 or abs(left_depth - right_depth) > 1:
return -1 # -1 반환
return max(left_depth, right_depth) + 1 # 양쪽 중 더 깊은 서브트리의 깊이에 +1
return compare_depth(root) != -1 # -1이면 불균형, 그렇지 않으면 균형
Runtime: 3 ms | Beats 88.20%
Memory: 88.20 MB | Beats 18.28%
잎 노드에서부터 깊이 계산을 시작하는 구조다. 잎 노드는 자식이 없어서 max(0, 0) + 1 = 1, 즉 깊이 값이 1이 된다.
개인적으로 지금까지 했던 트리 문제 중에 가장 어려웠던 문제였다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
return self.height(root) != -1
def height(self, node: TreeNode) -> int:
if not node:
return 0 # Base case: empty tree has height 0
# Recursively get the height of the left subtree
leftHeight = self.height(node.left)
if leftHeight == -1:
return -1 # If the left subtree is unbalanced, return -1
# Recursively get the height of the right subtree
rightHeight = self.height(node.right)
if rightHeight == -1:
return -1 # If the right subtree is unbalanced, return -1
# If the height difference between left and right subtrees is more than 1, return -1
if abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1:
return -1
# Return the height of the current node
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(𝑛) ← 최악의 경우(트리가 완전히 한 쪽으로 치우쳐서 모든 노드를 순회)
2nd
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root):
self.Bal = True
def dfs(node):
if not node: return 0
lft, rgh = dfs(node.left), dfs(node.right)
if abs(lft - rgh) > 1: self.Bal = False
return max(lft, rgh) + 1
dfs(root)
return self.Bal
self.Bal로 불균형 여부를 추적하는 방법은 처음 봐서 참고해봤다.



Leave a comment