1252. Cells with Odd Values in a Matrix
Description
There is an m x n matrix that is initialized to all 0’s. There is also a 2D array indices where each indices[i] = [ri, ci] represents a 0-indexed location to perform some increment operations on the matrix.
For each location indices[i], do both of the following:
- Increment all the cells on row ri.
- Increment all the cells on column ci.
Given m, n, and indices, return the number of odd-valued cells in the matrix after applying the increment to all locations in indices.
Example 1:
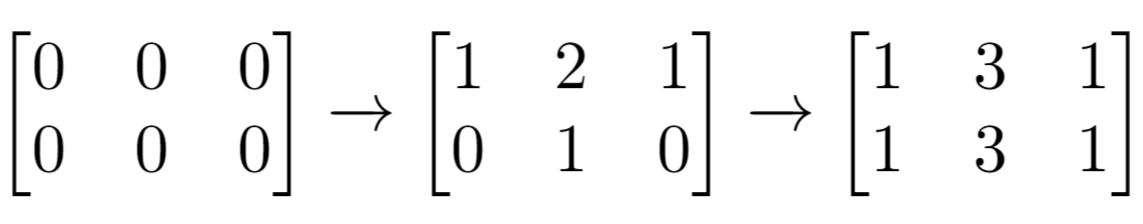
- Input: m = 2, n = 3, indices = [[0,1],[1,1]]
- Output: 6
- Explanation: Initial matrix = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]].
After applying first increment it becomes [[1,2,1],[0,1,0]].
The final matrix is [[1,3,1],[1,3,1]], which contains 6 odd numbers.
Example 2:
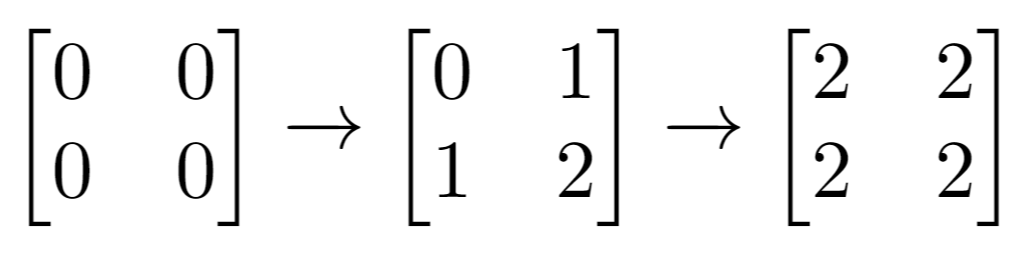
- Input: m = 2, n = 2, indices = [[1,1],[0,0]]
- Output: 0
- Explanation: Final matrix = [[2,2],[2,2]]. There are no odd numbers in the final matrix.
Constraints:
- 1 <= m, n <= 50
- 1 <= indices.length <= 100
- 0 <= ri < m
- 0 <= ci < n
Follow up: Could you solve this in O(n + m + indices.length) time with only O(n + m) extra space?
💡 Hint 1:
Simulation : With small constraints, it is possible to apply changes to each row and column and count odd cells after applying it.
💡 Hint 2:
You can accumulate the number you should add to each row and column and then you can count the number of odd cells.
Submitted Code
class Solution:
def oddCells(self, m: int, n: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int:
rows, cols = [0]*m, [0]*n
for x,y in indices: # O(l)
rows[x] += 1
cols[y] += 1
odd_rows = sum(r % 2 for r in rows) # O(m)
odd_cols = sum(c % 2 for c in cols) # O(n)
even_rows = m - odd_rows
even_cols = n - odd_cols
return odd_rows * even_cols + even_rows * odd_cols
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 19.36 MB | Beats 12.10%
행렬을 이중 for문 루프로 탐색하면 O(n * m + indices.length) 시간이 소요된다. 리트코드 예제는 행렬 크기가 작아서 이렇게 해도 runtime은 0ms로 나오지만 문제에서 요구하는 최적화된 되기 때문에 문제에서 요구하는 최적화된 방법은 아니다. 이 방법은 모든 행과 열을 탐색하지 않고 홀수 행 × 짝수 열 + 짝수 행 × 홀수 열로 빠르게 홀수인 값만 계산할 수 있다.
Other Solutions
1st
def oddCells(self, n: int, m: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int:
odd_rows, odd_cols, cntRow, cntCol = [False] * n, [False] * m, 0, 0
for r, c in indices:
odd_rows[r] ^= True
odd_cols[c] ^= True
cntRow += 1 if odd_rows[r] else -1 # 홀수 행 개수 갱신
cntCol += 1 if odd_cols[c] else -1 # 홀수 열 개수 갱신
# return m * cntRow + n * cntCol - 2 * cntRow * cntCol
return (m - cntCol) * cntRow + (n - cntRow) * cntCol
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑚+𝑛+𝓁)
space complexity: 𝑂(𝑚+𝑛)
카운트를 누적하는 대신 각 행과 열의 홀수/짝수 상태만 관리하고 홀수 행/열의 개수도 바로 갱신하는 방법도 있다.



Leave a comment