1260. Shift 2D Grid
Description
Given a 2D grid of size m x n and an integer k. You need to shift the grid k times.
In one shift operation:
- Element at
grid[i][j]moves togrid[i][j + 1]. - Element at
grid[i][n - 1]moves togrid[i + 1][0]. - Element at
grid[m - 1][n - 1]moves togrid[0][0].
Return the 2D grid after applying shift operation k times.
Example 1:
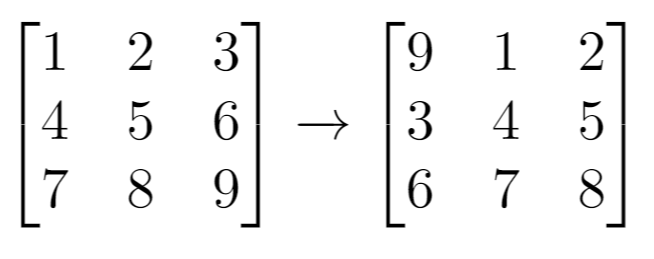
- Input:
grid= [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]],k= 1 - Output: [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]
Example 2:
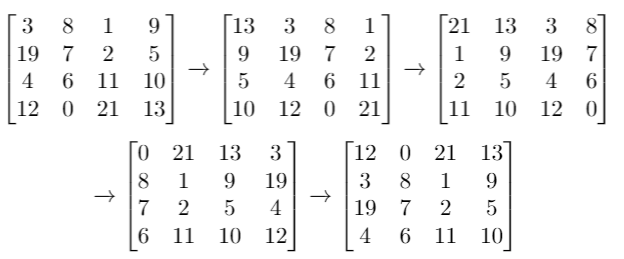
- Input:
grid= [[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]],k= 4 - Output: [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]
Example 3:
- Input:
grid= [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]],k= 9 - Output: [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Constraints:
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m <= 50
- 1 <= n <= 50
- -1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 1000
- 0 <= k <= 100
💡 Hint 1:
Simulate step by step. move grid[i][j] to grid[i][j+1]. handle last column of the grid.
💡 Hint 2:
Put the matrix row by row to a vector. take k % vector.length and move last k of the vector to the beginning. put the vector to the matrix back the same way.
Submitted Code
class Solution:
def shiftGrid(self, grid: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
moves = k % (m * n) # 완전한 한 바퀴를 모두 돌고 남은 이동 수
if moves == 0: # 남은 이동 수가 0이면 바꿀 필요 없음
return grid
result = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)] # 빈 2차원 리스트 생성
vector = [cell for row in grid for cell in row] # 2차원 -> 1차원
shifted_vector = vector[-moves:] + vector[:-moves] # moves만큼 뒷부분을 잘라서 앞에 붙임
for i in range(m * n):
result[i // n][i % n] = shifted_vector[i] # 1차원 -> 2차원
return result
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 19.69 MB | Beats 10.62%
2차원 그리드를 1차원으로 펼쳐 오른쪽으로 moves만큼 칸을 이동시킨 뒤, 다시 원래 크기의 2차원 그리드로 재구성하는 방법이다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def shiftGrid(self, grid: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
nRows, nCols = len(grid), len(grid[0])
k %= nRows * nCols
if k == 0: return grid
n = nRows * nCols
def reverse(grid, left, right):
while left < right:
grid[left//nCols][left%nCols], grid[right//nCols][right%nCols] = grid[right//nCols][right%nCols], grid[left//nCols][left%nCols]
left += 1
right -= 1
reverse(grid, 0, n-1)
reverse(grid, 0, k-1)
reverse(grid, k, n-1)
return grid
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑚+𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(1)
‘오른쪽으로 k칸 이동’을 배열을 뒤집는 것으로도 구현할 수 있다.
grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
k = 3
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
[9,8,7|6,5,4,3,2,1] ← reverse(grid, 0, n-1)
[7,8,9|6,5,4,3,2,1] ← reverse(grid, 0, k-1)
[7,8,9|1,2,3,4,5,6] ← reverse(grid, k, n-1)
k
return [[7,8,9],[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]



Leave a comment