144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
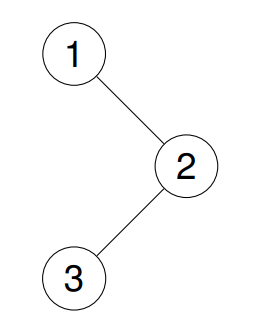
Example 1:
- Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
- Output: [1,2,3]
- Explanation:
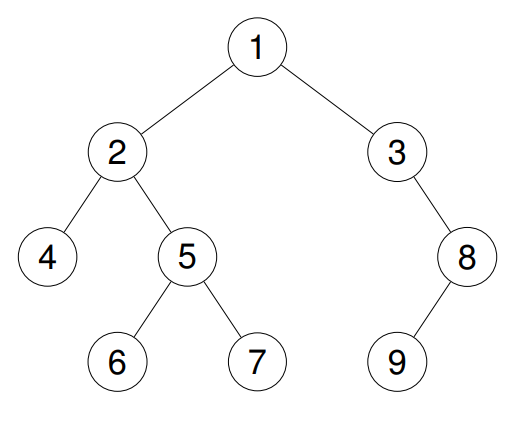
Example 2:
- Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
- Output: [1,2,4,5,6,7,3,8,9]
- Explanation:
Example 3:
- Input: root = []
- Output: []
Example 4:
- Input: root = [1]
- Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def preorderTraversal(self, root):
"""
:type root: Optional[TreeNode]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
order = [] # 순서 저장
stack = [] # 스택
while root:
order.append(root.val) # 가장 먼저 해당 노드의 값 저장(루트)
if root.left and root.right: # 노드에 왼쪽과 오른쪽 자식이 모두 있다면
stack.append(root) # 해당 노드를 스택에 저장하고
root = root.left # 왼쪽 자식으로 이동
elif root.left and not root.right: # 노드에 왼쪽 자식만 있다면
root = root.left # 바로 왼쪽 자식으로 이동
elif not root.left and root.right: # 노드에 오른쪽 자식만 있다면
root = root.right # 바로 오른쪽 자식으로 이동
else: # 노드에 자식이 없고
if stack: # 스택이 있을 경우
root = stack.pop() # 스택에 마지막으로 저장된 노드로 이동하고
root = root.right # 오른쪽 자식으로 이동
else: # 스택이 없을 경우
return order # 순회 종료
return order # 빈 트리일 경우
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 12.36 MB | Beats 92.46%
문제에서 요구하는 대로 재귀 호출 없이 스택으로 풀어봤다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def preorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
res = []
if not root: # 빈 트리일 경우
return res
st = [root] # 루트 노드를 저장한 상태로 스택 초기화
while st: # 스택이 있는 동안 반복
node = st.pop() # 스택의 마지막 노드를 꺼낸 후 이동
res.append(node.val) # 해당 노드의 값을 결과에 저장
if node.right: # 오른쪽 자식이 있을 경우 스택에 저장
st.append(node.right)
if node.left: # 왼쪽 자식이 있을 경우 스택에 저장
st.append(node.left)
return res
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
제출했던 답안보다 간단히 할 수 있는 방법을 참고했다.
2nd
class Solution:
def preorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
res = []
def preorder(node):
if not node:
return
res.append(node.val) # 부모 노드의 값을 순서에 저장
preorder(node.left) # 왼쪽 자식으로 이동해서 재귀 호출
preorder(node.right) # 오른쪽 자식으로 이동해서 재귀 호출
preorder(root)
return res
재귀 호출로 이진 트리의 순회를 구현하는 것도 중요하기 때문에 짚고 넘어갔다.



Leave a comment