257. Binary Tree Paths
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
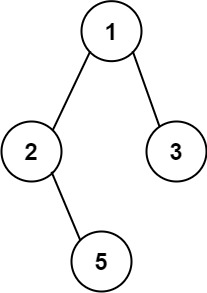
- Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5]
- Output: [“1->2->5”,”1->3”]
Example 2:
- Input: root = [1]
- Output: [“1”]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
"""
:type root: Optional[TreeNode]
:rtype: List[str]
"""
def find_leaf(node, path):
if not node:
return
# 현재 경로 업데이트
if path:
path += "->{}".format(str(node.val))
else:
path = str(node.val)
# 잎노드 도달 여부
if not node.left and not node.right:
result.append(path)
else:
find_leaf(node.left, path)
find_leaf(node.right, path)
result = []
find_leaf(root, "")
return result
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 12.44 MB | Beats 76.80%
재귀호출로 깊이우선탐색을 했다.
root = [1,2,3,null,5]
1
/ \
2 3
\
5
node path
find_leaf(root, "") 1 "1"
find_leaf(2, "1") 2 "1->2"
find_leaf(null, "1->2") (return)
find_leaf(5, "1->2") 5 "1->2->5" (result + path)
find_leaf(3, "1") 3 "1->3" (resukt + path)
result = [“1->2->5”,”1->3”]
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution(object):
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
res = []
if not root:
return res
stack = [(root, str(root.val))] # 스택에 (현재 노드, 지금까지의 경로)를 튜플로 저장
while stack:
node, path = stack.pop() # 가장 최근에 넣은 튜플 꺼내기
if not node.left and not node.right: # 잎노드이면 지금까지의 경로를 결과에 저장
res.append(path)
if node.right: # 오른쪽 자식 먼저 저장(왼쪽 먼저 탐색해야 하기 때문)
stack.append((node.right, path + "->" + str(node.right.val)))
if node.left: # 왼쪽 자식 저장
stack.append((node.left, path + "->" + str(node.left.val)))
return res
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
재귀 없이 스택으로 깊이우선탐색을 하는 방법도 있다.
root = [1,2,3,null,5]
1 / \ 2 3 \ 5 stack = [(1, "1")] pop() -> (1, "1") right(3) push → (3, "1->3") left(2) push → (2, "1->2") pop() -> (2, "1->2") right(5) push → (5, "1->2->5") pop() -> (5, "1->2->5") leaf → result + "1->2->5" pop() -> (3, "1->3") leaf → result + "1->3"
result = [“1->2->5”,”1->3”]



Leave a comment