463. Island Perimeter
Description
You are given row x col grid representing a map where grid[i][j] = 1 represents land and grid[i][j] = 0 represents water.
Grid cells are connected horizontally/vertically (not diagonally). The grid is completely surrounded by water, and there is exactly one island (i.e., one or more connected land cells).
The island doesn’t have “lakes”, meaning the water inside isn’t connected to the water around the island. One cell is a square with side length 1. The grid is rectangular, width and height don’t exceed 100. Determine the perimeter of the island.
Example 1:
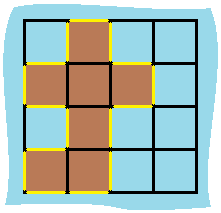
- Input: grid = [[0,1,0,0],[1,1,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]]
- Output: 16
- Explanation: The perimeter is the 16 yellow stripes in the image above.
Example 2:
- Input: grid = [[1]]
- Output: 4
Example 3:
- Input: grid = [[1,0]]
- Output: 4
Constraints:
- row == grid.length
- col == grid[i].length
- 1 <= row, col <= 100
- grid[i][j] is
0or1. - There is exactly one island in
grid.
Submitted Code
class Solution(object):
def islandPerimeter(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
perimeter = 0
row = len(grid) # 행
col = len(grid[0]) # 열
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if grid[i][j] == 1: # 해당 칸이 땅일 때만
up = 1 if (i == 0 or grid[i-1][j] == 0) else 0 # 윗면
down = 1 if (i == row-1 or grid[i+1][j] == 0) else 0 # 아랫면
left = 1 if (j == 0 or grid[i][j-1] == 0) else 0 # 왼쪽 옆면
right = 1 if (j == col-1 or grid[i][j+1] == 0) else 0 # 오른쪽 옆면
perimeter += (up + down + left + right)
return perimeter
Runtime: 51 ms | Beats 61.53%
Memory: 12.58 MB | Beats 93.19%
그리드 전체를 이중 루프로 완전 탐색하는 Brute Force 방식이다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def islandPerimeter(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
perimeter = 0
rows, cols = len(grid), len(grid[0])
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
if grid[r][c] == 1:
perimeter += 4
if r > 0 and grid[r-1][c] == 1:
perimeter -= 2
if c > 0 and grid[r][c-1] == 1:
perimeter -= 2
return perimeter
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑚*𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(1)
해당 칸일 땅일 경우 기본적으로 4변이 있다고 가정한 후, 이미 계산된 위쪽 또는 왼쪽 이웃 칸이 땅이라면 2변(현재 칸 1변 + 상대 칸 1변)을 빼주는 아이디어를 사용했다. 위쪽과 왼쪽만 검사하기 때문에 위의 코드보다 조금 더 최적화됐다.
2nd
class Solution:
def islandPerimeter(self, grid):
m, n, Perimeter = len(grid), len(grid[0]), 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
Perimeter += 4*grid[i][j]
if i > 0: Perimeter -= grid[i][j]*grid[i-1][j]
if i < m-1: Perimeter -= grid[i][j]*grid[i+1][j]
if j > 0: Perimeter -= grid[i][j]*grid[i][j-1]
if j < n-1: Perimeter -= grid[i][j]*grid[i][j+1]
return Perimeter
조금 더 수학적인 방식으로, 위/아래/왼쪽/오른쪽 이웃이 땅이면 그만큼 공유되는 변만큼 빼주는 것은 같지만 곱셈을 이용하여 분기 없이 간단히 했다. grid[i][j]가 0이면 아무 것도 빼지 않고, grid[i][j]가 1이고 이웃이 1이면 1 * 1 = 1 이기 때문에 변을 하나 빼면 된다.
3rd
class Solution:
def islandPerimeter(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
rows, cols = len(grid), len(grid[0])
perimeter = 0
def dfs(r, c):
# 현재 위치가 경계를 벗어나거나 물이라면 섬의 가장자리 -> +1
if r < 0 or r >= rows or c < 0 or c >= cols or grid[r][c] == 0:
return 1
# 이미 방문한 땅(-1로 마킹됨) -> 세지 않음
if grid[r][c] == -1:
return 0
grid[r][c] = -1
return (dfs(r + 1, c) +
dfs(r - 1, c) +
dfs(r, c + 1) +
dfs(r, c - 1))
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
if grid[r][c] == 1:
perimeter += dfs(r, c)
return perimeter
섬(1)을 DFS로 탐색하면서, 각 경계 또는 물(0)을 만날 때마다 둘레 +1을 세는 방식이다.
4th
class Solution:
def islandPerimeter(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
row, col, queue = len(grid), len(grid[0]), deque()
for x in range(row):
for y in range(col):
if grid[x][y] == 1:
queue.append((x,y))
return self.bfs(grid, row, col, queue)
def bfs(self,grid, row, col, queue):
visited = set() # 중복 방문 방지용
perimeter = 0
while queue:
x,y = queue.popleft()
if (x,y) in visited: continue
visited.add((x,y))
for nx,ny in [[x+1,y],[x-1,y],[x,y+1],[x,y-1]]:
if 0<=nx<row and 0<=ny<col:
if grid[nx][ny] == 0:
perimeter+=1
if grid[nx][ny] == 1:
queue.append((nx,ny))
else: # if out of grid
perimeter+=1
return perimeter
큐를 사용하여 BFS 방식으로 탐색하는 방법이다. 먼저 섬의 첫 번째 땅(1)을 찾은 뒤 거기서부터 탐색한다.



Leave a comment