501. Find Mode in Binary Search Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary search tree (BST) with duplicates, return all the mode(s) (i.e., the most frequently occurred element) in it.
If the tree has more than one mode, return them in any order.
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than or equal to the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node’s key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
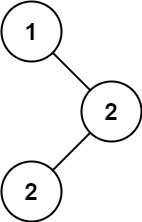
- Input: root = [1,null,2,2]
- Output: [2]
Example 2:
- Input: root = [0]
- Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Follow up: Could you do that without using any extra space? (Assume that the implicit stack space incurred due to recursion does not count).
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def findMode(self, root):
"""
:type root: Optional[TreeNode]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
count = {}
result = []
def dfs(node):
if not node:
return
count[node.val] = count.get(node.val, 0) + 1
search(node.left)
search(node.right)
dfs(root)
max_count = max(count.values()) # 최빈값
for val, freq in count.items():
if freq == max_count: # 최빈값과 같으면 결과에 추가
result.append(val)
return result
Runtime: 14 ms | Beats 15.08%
Memory: 20.72 MB | Beats 8.52%
재귀 함수를 만들어서 트리를 순회하고, 딕셔너리로 각 노드의 빈도수를 저장했다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def findMode(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
def in_order_traversal(node):
nonlocal current_val, current_count, max_count, modes
if not node:
return
in_order_traversal(node.left)
# 현재 노드의 카운트 값이 이전과 같으면 +1, 다르면 1로 초기화하고 현재 노드로 갱신
current_count = current_count + 1 if node.val == current_val else 1
current_val = node.val
if current_count > max_count: # 지금까지 본 것 중 가장 많이 나온 값이면 새 리스트로 갱신
max_count = current_count
modes = [current_val]
elif current_count == max_count: # 최빈값과 같다면 리스트에 추가
modes.append(current_val)
in_order_traversal(node.right)
current_val = None
current_count = 0
max_count = 0
modes = []
in_order_traversal(root)
return modes
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(ℎ)
BST를 중위 순회하면 값들이 정렬된 순서(오름차순)로 나온다는 것을 이용한 방법으로 딕셔너리 없이도 구현할 수 있다. (왼쪽 서브트리-현재 노드-오른쪽 서브트리) 순서로 순회하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
root = [1,null,2,2]
1 \ 2 / 2 current_val : None → 1 current_count : 0 → 1 max_count : 0 → 1 modes = [1] current_val : 1 → 2 node.val != current_val → current_count = 1 current_count == max_count → modes.append(2) modes = [1, 2] current_val : 2 → 2 node.val == current_val → current_count = 2 current_count > max_count → max_count = 2 modes = [2]
modes = [2]



Leave a comment