637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
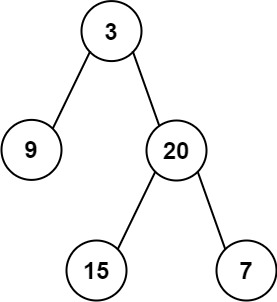
- Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
- Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
- Explanation: The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11. Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Example 2:
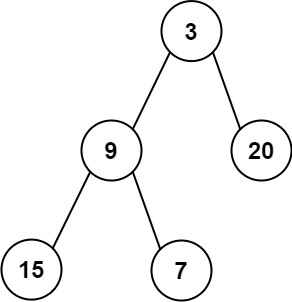
- Input: root = [3,9,20,15,7]
- Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
- -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def averageOfLevels(self, root):
"""
:type root: Optional[TreeNode]
:rtype: List[float]
"""
queue = deque([root])
result = []
while queue:
quantity = len(queue) # 해당 레벨의 노드 개수
val_sum = 0 # 해당 레벨의 노드 값 합산
for _ in range(quantity):
node = queue.popleft()
val_sum += node.val
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
average = float(val_sum) / quantity # Python3에서는 형변환 필요없음
result.append(average)
return result
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 17.26 MB | Beats 19.34%
너비 우선 탐색 방식으로 각 레벨에 접근했다. Python2에서 / 연산자를 사용하면 두 값 모두 정수일 경우 소수점이 버려지기 때문에 float로 형변환을 해야 했다.
Other Solutions
1st
def averageOfLevels(self, root):
info = []
def dfs(node, depth = 0):
if node:
if len(info) <= depth: # 해당 깊이의 (노드 값의 합, 노드 수) 쌍을 저장할 공간 창조
info.append([0, 0])
info[depth][0] += node.val
info[depth][1] += 1
dfs(node.left, depth + 1)
dfs(node.right, depth + 1)
dfs(root)
return [s/float(c) for s, c in info]
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(𝑛)
DFS 방식을 사용한 답안도 참고했다. Example 1의 경우 info 리스트의 최종 형태는 [[3, 1], [29, 2], [22, 2]]이 된다.



Leave a comment