700. Search in a Binary Search Tree
Description
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST) and an integer val.
Find the node in the BST that the node’s value equals val and return the subtree rooted with that node. If such a node does not exist, return null.
Example 1:
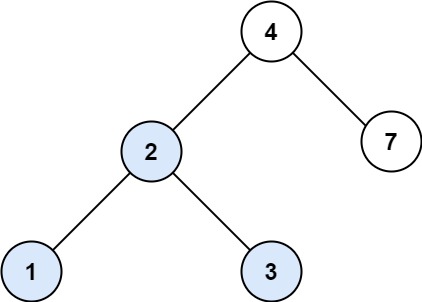
- Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
- Output: [2,1,3]
Example 2:
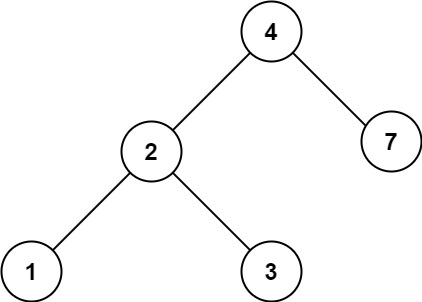
- Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
- Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5000]. - 1 <= Node.val <= 107
rootis a binary search tree.- 1 <= val <= 107
Submitted Code
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def searchBST(self, root, val):
"""
:type root: Optional[TreeNode]
:type val: int
:rtype: Optional[TreeNode]
"""
if not root:
return None
if root.val == val:
return root
elif root.val > val: # val이 현재 노드값보다 작으면 왼쪽 이동
return self.searchBST(root.left, val)
else: # val이 현재 노드값보다 크면 오른쪽 이동
return self.searchBST(root.right, val)
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 16.46 MB | Beats 60.34%
문제 설명의 Output: [2,1,3] 부분 때문에 따로 리스트를 만드는 것인줄 알았는데, 리턴 타입이 TreeNode로 명시되어있기 때문에 에러가 발생한다. 특정 노드의 서브트리는 그냥 그 노드 객체 자체를 리턴하면 되고 null을 리턴하려면 아무것도 리턴하지 않으면 된다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution:
def searchBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
while root: # 노드가 존재하는 동안 탐색
if root.val == val:
return root
elif val < root.val:
root = root.left
else:
root = root.right
return None # val과 일치하는 노드 없음
time complexity: 𝑂(ℎ)
space complexity: 𝑂(1)
while문을 사용하면 재귀 호출 없이 탐색하기 때문에 메모리를 더 절약할 수 있다.



Leave a comment