766. Toeplitz Matrix
Description
Given an m x n matrix, return true if the matrix is Toeplitz. Otherwise, return false.
A matrix is Toeplitz if every diagonal from top-left to bottom-right has the same elements.
Example 1:
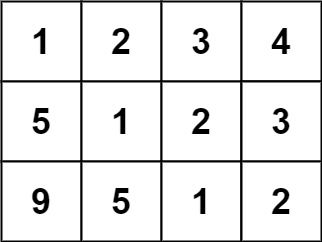
- Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,1,2,3],[9,5,1,2]]
- Output: true
- Explanation:
In the above grid, the diagonals are:
“[9]”, “[5, 5]”, “[1, 1, 1]”, “[2, 2, 2]”, “[3, 3]”, “[4]”.
In each diagonal all elements are the same, so the answer is True.
Example 2:
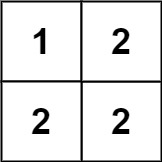
- Input: matrix = [[1,2],[2,2]]
- Output: false
- Explanation:
The diagonal “[1, 2]” has different elements.
Constraints:
- m == matrix.length
- n == matrix[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 20
- 0 <= matrix[i][j] <= 99
Follow up:
- What if the matrix is stored on disk, and the memory is limited such that you can only load at most one row of the matrix into the memory at once?
- What if the matrix is so large that you can only load up a partial row into the memory at once?
💡 Hint 1:
Check whether each value is equal to the value of it's top-left neighbor.
Submitted Code
class Solution(object):
def isToeplitzMatrix(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: bool
"""
rows = len(matrix)
cols = len(matrix[0])
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
# 오른쪽 사선 아래 원소가 존재하고 두 원소의 값이 다르다면 False 반환
if (i < rows-1 and j < cols-1) and matrix[i][j] != matrix[i+1][j+1]:
return False
return True
Runtime: 0 ms | Beats 100.00%
Memory: 12.38 MB | Beats 89.13%
모든 원소를 순회하며 오른쪽 사선 아래의 원소와 값을 비교하는 방법을 사용했다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution(object):
def isToeplitzMatrix(self, matrix):
for i in range(1, len(matrix)):
for j in range(1, len(matrix[0])):
if matrix[i][j] != matrix[i-1][j-1]:
return False
return True
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑚*𝑛)
space complexity: 𝑂(1)
순회하는 시작점을 변경하면 더 깔끔하게 작성할 수 있다.
2nd
class Solution:
def isToeplitzMatrix(self, m: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
# compare each row to the next row shifted by 1
return all(r1[:-1] == r2[1:] for r1,r2 in zip(m, m[1:]))
위아래로 인접한 두 행을 각각 앞뒤로 밀어서 겹치는 부분이 일치하는지 확인하는 방법이다.
m = [[1,2,3,4],[5,1,2,3],[9,5,1,2]]
m m[1:] zip(m, m[1:])
[[1,2,3,4], [[5,1,2,3], (([1,2,3,4], [5,1,2,3]),
[5,1,2,3], [9,5,1,2]] ([5,1,2,3], [9,5,1,2]))
[9,5,1,2]]
r1[:-1] → [1,2,3 4] [5,1,2 3]
r2[1:] → [5 1,2,3] [9 5,1,2]
match match
return True



Leave a comment