883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
Description
You are given an n x n grid where we place some 1 x 1 x 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of the cell (i, j).
We view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes.
A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3-dimensional figure to a 2-dimensional plane. We are viewing the “shadow” when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return the total area of all three projections.
Example 1:
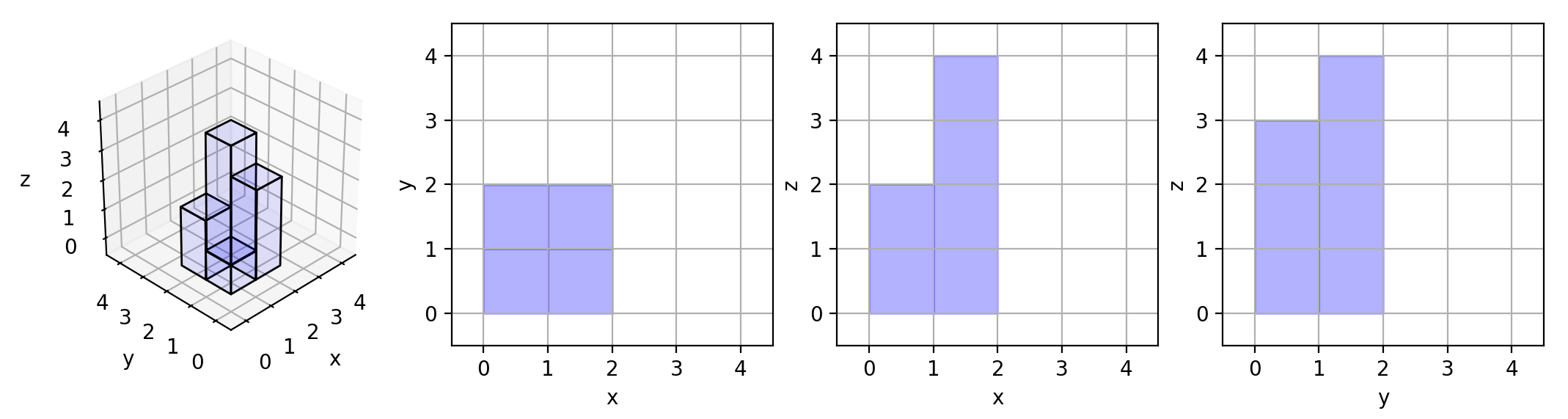
- Input: grid = [[1,2],[3,4]]
- Output: 17
- Explanation: Here are the three projections (“shadows”) of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
Example 2:
- Input: grid = [[2]]
- Output: 5
Example 3:
- Input: grid = [[1,0],[0,2]]
- Output: 8
Constraints:
- n == grid.length == grid[i].length
- 1 <= n <= 50
- 0 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
Submitted Code
class Solution(object):
def projectionArea(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(grid)
top, hor, ver = 0, 0, 0 # 윗면(xy), 옆면(zx), 앞면(zy)
for i in range(n):
row_max, col_max = 0, 0
for j in range(n):
top += 1 if grid[i][j] > 0 else 0 # 0보다 큰 셀의 개수
row_max = max(grid[i][j], row_max) # 각 행의 최댓값들의 합
col_max = max(grid[j][i], col_max) # 각 열의 최댓값들의 합
hor += row_max
ver += col_max
return top + hor + ver
Runtime: 3 ms | Beats 76.60%
Memory: 12.44 MB | Beats 67.02%
행과 열의 길이가 똑같은 행렬이기 때문에 행과 열의 인덱스를 서로 바꿔주기만 하면 한 행이나 열에서 최댓값을 찾을 수 있다.
Other Solutions
1st
class Solution(object):
def projectionArea(self, grid):
hor = sum(map(max, grid)) # 각 행의 최대값들의 합
ver = sum(map(max, zip(*grid))) # 각 열의 최대값들의 합
top = sum(v > 0 for row in grid for v in row) # xy 평면의 면적
return ver + hor + top
class Solution(object):
def projectionArea(self, grid):
return sum(map(max, grid + zip(*grid))) + sum(v > 0 for row in grid for v in row)
time complexity: 𝑂(𝑛2)
space complexity: 𝑂(1)
같은 원리이지만 좀 더 파이썬스럽게 작성된 코드를 참고했다. zip(*grid)에서 언패킹 연산자 *가 들어간 *grid는 리스트를 풀어서 인자로 전달하고, zip()으로 각 열 단위를 튜플로 묶어준다.



Leave a comment